CM-Well Spark Connector¶
Introduction¶
Apache Spark is a tool for processing and analyzing big data quickly, efficiently and easily. The two main Spark data structures that the Spark Connector uses are:
- RDD - Resilient Distributed Dataset. This is a data structure that can be distributed over several machines, using data in memory or in disk storage. An RDD must be tolerant to errors that may occur when accessing one of its partitions.
- Data Frame - Data stored in a table (two-dimensional matrix) format.
The RDD class supports many functions for manipulating data and performing statistical operations such as counting, aggregating, mapping and reducing, grouping, filtering and so on.
The CM-Well Spark Connector is an add-on to the Spark engine, which allows you to retrieve infotons by CM-Well query, insert them into an RDD or Data Frame object, and run those objects' processing and analysis functions on the data.
To learn more about Spark classes and functions, please visit the Apache Spark web site.
Comparison to Other Advanced Query Tools¶
You may be familiar with other special tools for querying and performing statistical analysis on CM-Well data. Here is a brief explanation about when to use each tool.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| stats API | The stats API provides access to statistical values from CM-Well's underlying indexing module. The statistics refer to infoton field values, and include metrics such as cardinality, minimum, maximum, average, top frequent terms, and so on (see Query with Data Statistics to learn more). CM-Well maintains inverted-indexes and updates these values in an ongoing manner, so that retrieving them is very fast and doesn't require iterating over infotons. In the interest of performance, use the stats API if you only need one of the basic metrics it supports. |
| SPARQL queries (_sp endpoint) | SPARQL is effective for queries that require graph traversal, i.e. exploring infotons' inbound and outbound links, on a limited portion of the data graph. Use this API to apply SPARQL queries to a particular path in CM-Well. See Apply SPARQL to Query Results to learn more. |
| SPARQL queries on whole graph (_sparql endpoint) | Same as above, except that this endpoint can handle queries on the entire CM-Well graph as opposed to a particular path. See Apply SPARQL to the Entire Graph to learn more. |
| Spark Connector | Use the Spark Connector to run statistical queries on all of CM-Well, or on large parts of it. There is no limit (apart from the underlying hardware) on the data size or query complexity that Spark can handle. (As mentioned above, use the stats API if you only need one of the metrics it provides.) |
System Requirements¶
To run the Spark Connector, you will need a Linux environment and JVM 1.8.
Note
- An easy way to run the Spark Connector on a non-Linux machine is to install the Docker utility, which provides a virtual Linux environment.
- Depending on the Spark query you're running and the amount of data, the query may require large amounts of memory. Make sure to configure the JVM correctly to accommodate for the required memory size.
- The Spark Connector package contains Scala 2.12.4 and Spark 2.1.
Downloading and Installing the Spark Connector¶
Coming soon.
Running the CM-Well Connector in the Spark Client¶
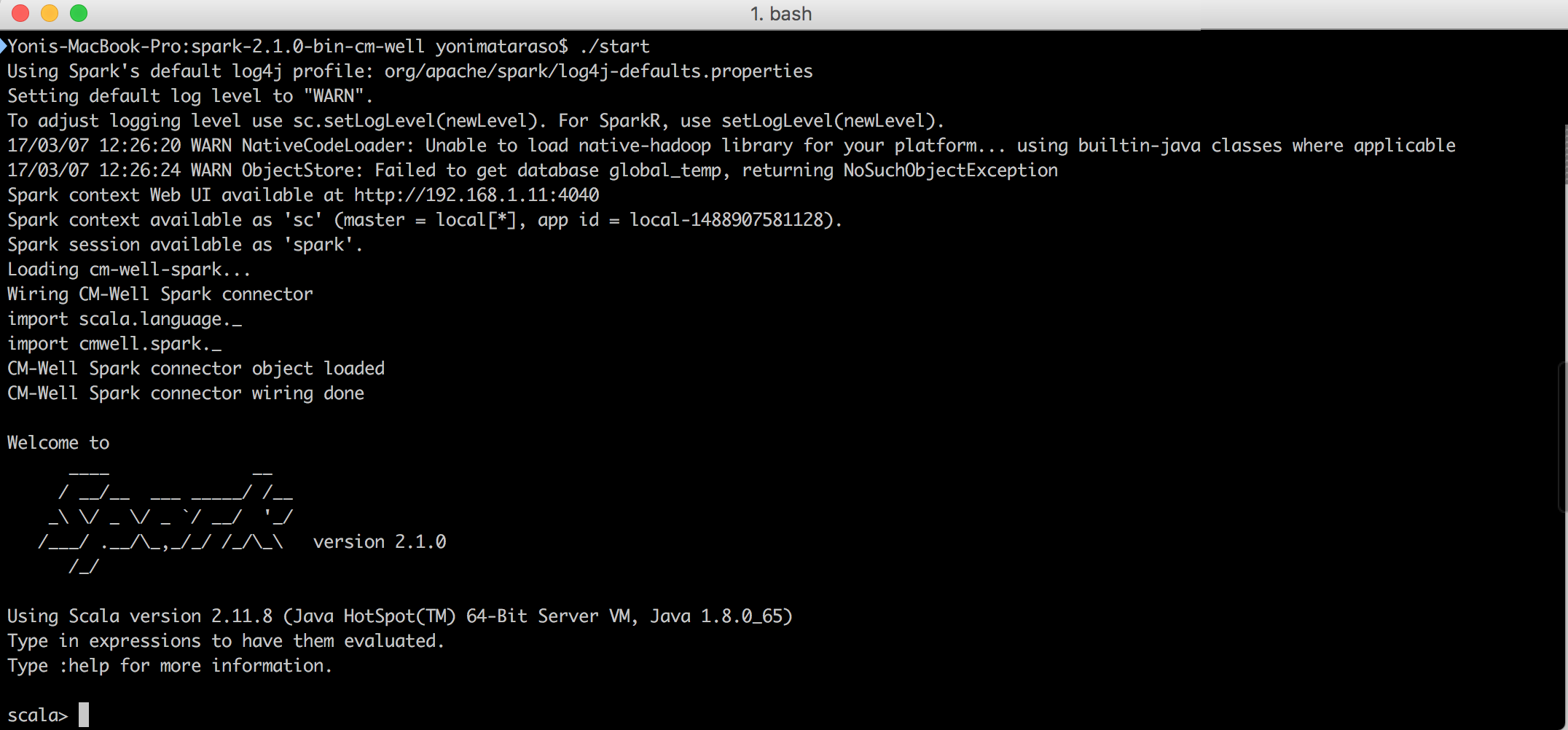
To run the Spark server and initialize the CM-Well Spark Connector, run the start script in the root directory of the Spark Connector installation (the root directory is named spark-2.1.0-bin-cm-well). The script runs the Scala interactive shell and initializes the built-in Spark Connector module. You can now run Spark commands in the Scala REPL mode.
This is what the Spark Connector Scala shell looks like when you first run it:
Here is an example of calling a CMWell object function to create an RDD from an infoton space:
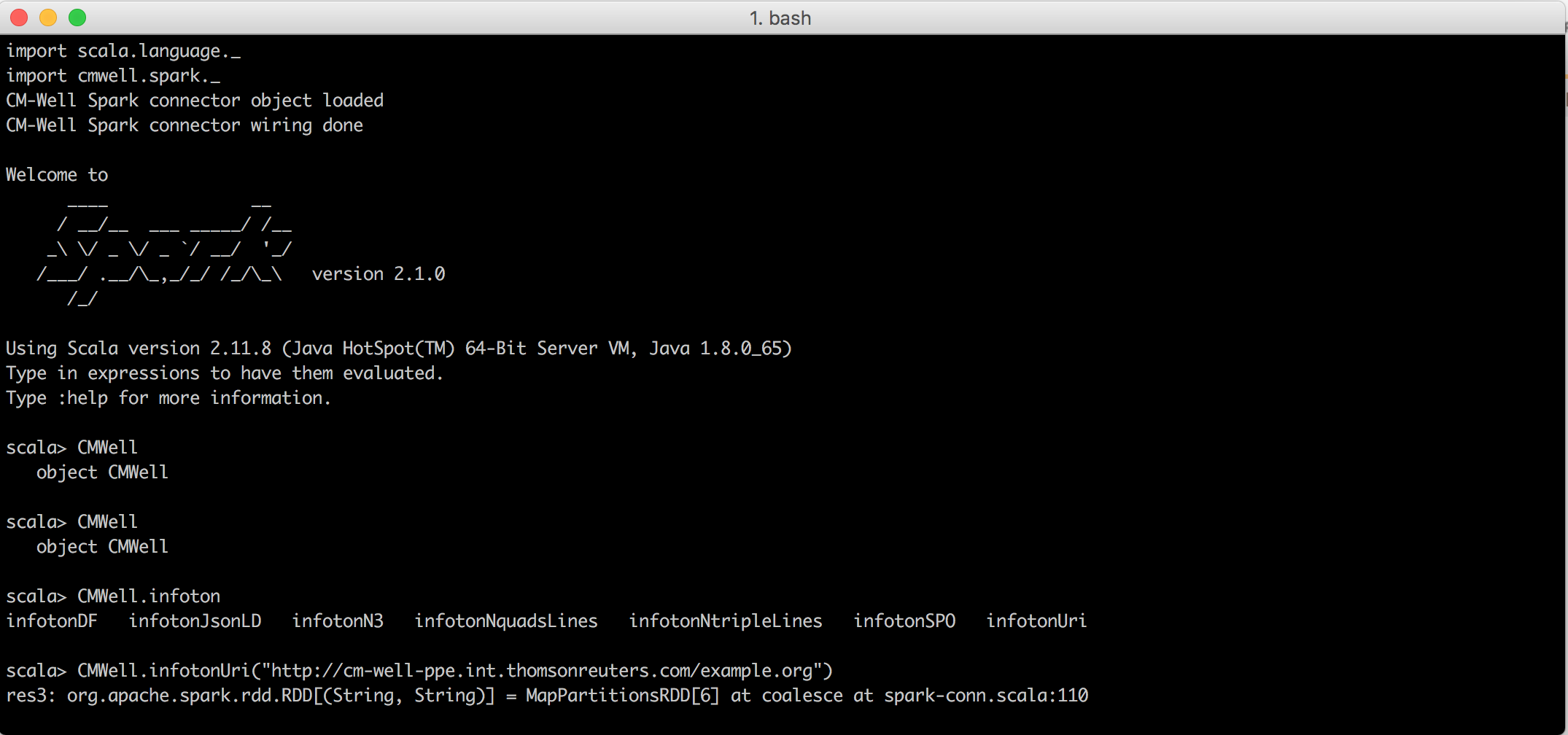
The CM-Well Object Interface¶
The CM-Well Spark Connector interface is encapsulated in the CMWell object. All of the object's functions receive a CM-Well URI and optionally a query, and return a Spark RDD or Data Frame object that represent the "infoton space" (set of infotons) that matches the path and query. You can then run all the functions that Spark supports for its RDD and DataFrame classes. (See the Spark Programming Guide to learn more.)
All CMWell functions take the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| cmWellUrl | Mandatory. The CM-Well path from which to take the infotons. |
| qp | Optional. A query with which to filter the infotons under cmWellUrl. See CM-Well Query Parameters to learn more about query parameter syntax. |
| infotonLimit | Optional. The maximal number of infotons to retrieve (the default is 3000). We recommend using the default during development, then setting the limit to 0 (indicating no limit) for production. |
Note
- Currently the Spark Connector assumes correct usage of the CM-Well API (valid URIs, valid query syntax and so on). There are no validity checks or detailed error messages.
- We recommend using the "named parameter" syntax when calling CMWell functions, as follows:
infotonUri(cmWellUrl="<cm-well-host>/example.org", qp=null, infotonLimit=100);. This allows you to provide the parameters in any order, and to omit optional parameters.
The following table describes the CMWell object's functions.
| Function | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| infotonUri(cmWellUrl:String, qp:String=null, infotonLimit:Int=INFOTON_SAFETY_LIMIT_WHEN_PLAYING) | RDD[(String, String)] | Returns an RDD of string pairs. The first string is the RDF URI of each infoton in the space; the second string is the CM-Well-based URL. |
| infotonNtripleLines(cmWellUrl:String, qp:String=null, infotonLimit:Int=INFOTON_SAFETY_LIMIT_WHEN_PLAYING) | RDD[String] | Returns an RDD of strings. Each string is a triple in N-Triples format, belonging to an infoton in the infoton space. All triples belonging to the same infoton appear in sequence. |
| infotonNquadsLines(cmWellUrl:String, qp:String=null, infotonLimit:Int=INFOTON_SAFETY_LIMIT_WHEN_PLAYING) | RDD[String] | As above, but each string is a quad, where the 4th value is the entity's sub-graph label. |
| infotonN3(cmWellUrl:String, qp:String=null, infotonLimit:Int=INFOTON_SAFETY_LIMIT_WHEN_PLAYING) | RDD[(String, String)] | Returns an RDD of string pairs. The first string is the RDF URI of each infoton in the space; the second string is the N3 representation the infoton. |
| infotonJsonLD(cmWellUrl:String, qp:String=null, infotonLimit:Int=INFOTON_SAFETY_LIMIT_WHEN_PLAYING) | RDD[(String, String)] | As above but with JSONLD infoton representation. |
| infotonDF(cmWellUrl:String, qp:String=null, infotonLimit:Int=INFOTON_SAFETY_LIMIT_WHEN_PLAYING) | DataFrame | Returns a DataFrame containing a tabular representation of all infotons in the infoton space. Each row is an infoton and each column is an infoton field. For best results, apply this function to infotons of the same type (with the same fields). If the infotons have different sets of fields, the Connector creates a union of all fields. |
Calling the Spark Connector from Your Code¶
You can also call the Spark Connector from your own code, then create a jar that you submit and run as a Spark job. To do this:
- Import the Spark package in your code. (Note: this must be Spark 2.1 or higher.)
- Add the cm-well-spark-conn_2.12-2.1.jar (contained in the Spark Connector zip download) to your project.
- Import the CMWell class.
- Initialize the Spark session.
- Call CMWell.wireInSpark(spark:SparkSession).
- Add Spark analysis code to your project as needed.
- Submit your job to Spark by using the spark-submit command. Learn more at http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/submitting-applications.html.
Note
You will need to include the Spark Connector jar in your project, either by including to it in jar dependencies when submitting the Spark job, or by packaging it in an assembly that you submit to Spark.